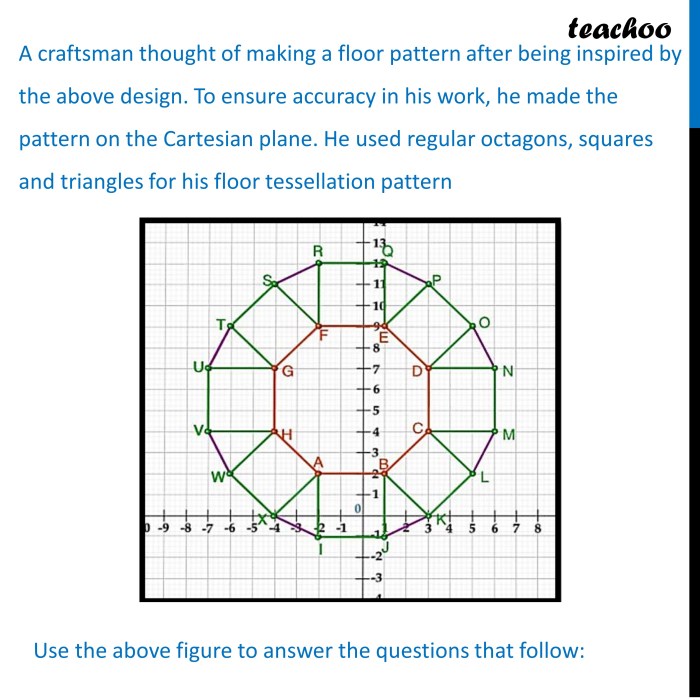
The figure above is a regular octagon, an eight-sided polygon with equal side lengths and equal interior angles. Regular octagons possess unique geometric properties, making them significant in various fields. This exploration delves into the characteristics, constructions, and applications of regular octagons, providing a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating shape.
Regular octagons exhibit remarkable symmetry, with eight lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 8. They have 8 sides, 8 vertices, and 20 diagonals, offering a balanced and aesthetically pleasing form.
Octagon Overview
A regular octagon is a polygon with eight equal sides and eight equal angles. It is a regular polygon, which means that all its sides and angles are equal. Regular octagons have a high degree of symmetry and are often used in architecture and design.
Sides and Angles
A regular octagon has eight sides and eight angles. The interior angles of a regular octagon measure 135 degrees, and the exterior angles measure 45 degrees.
Symmetry Properties
Regular octagons have a high degree of symmetry. They have eight lines of symmetry, which pass through opposite vertices and bisect the opposite sides. They also have eight rotational symmetries, which means that they can be rotated by 45 degrees around their center and still look the same.
Geometric Properties
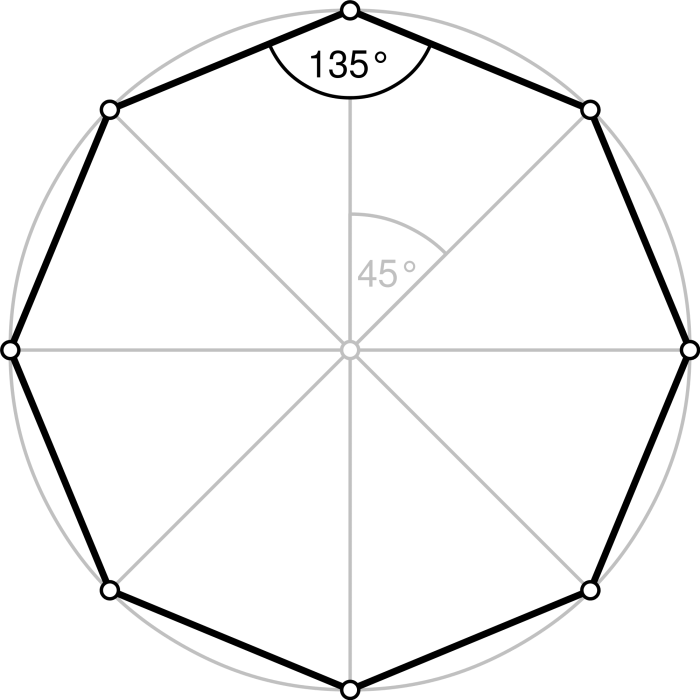
Interior and Exterior Angles
The interior angles of a regular octagon measure 135 degrees. This can be calculated using the formula:
$$(n-2) \times 180^\circ$$
where n is the number of sides.
The exterior angles of a regular octagon measure 45 degrees. This can be calculated using the formula:
$$360^\circ / n$$
where n is the number of sides.
Side Length and Apothem
The relationship between the side length (s) and the apothem (a) of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
$$a = \fracs2 \cot \left(\frac180^\circn\right)$$
where n is the number of sides.
Diagonals
A regular octagon has 20 diagonals. The diagonals can be classified into two types: long diagonals and short diagonals. The long diagonals connect opposite vertices, while the short diagonals connect adjacent vertices.
Area and Perimeter
Area
The area of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
$$A = 2s^2 \cot \left(\frac180^\circn\right)$$
where s is the side length and n is the number of sides.
Perimeter
The perimeter of a regular octagon can be calculated using the formula:
$$P = 8s$$
where s is the side length.
Table of Area and Perimeter
| Side Length | Area | Perimeter |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.828 | 8 |
| 2 | 11.314 | 16 |
| 3 | 25.981 | 24 |
Constructions: The Figure Above Is A Regular Octagon
Using a Compass and Straightedge
To construct a regular octagon using a compass and straightedge, follow these steps:
- Draw a circle.
- Divide the circle into eight equal parts using a protractor.
- Connect the points of division to form the octagon.
Golden Ratio
The Golden Ratio, also known as the Divine Proportion, is a special number approximately equal to 1.618. It is often used in art and architecture to create aesthetically pleasing designs.
The Golden Ratio can be used to construct a regular octagon by following these steps:
- Draw a square.
- Bisect one side of the square to create a golden rectangle.
- Divide the golden rectangle into two squares.
- Connect the corners of the two squares to form an octagon.
Step-by-Step Table, The figure above is a regular octagon
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Draw a circle. |
| 2 | Divide the circle into eight equal parts. |
| 3 | Connect the points of division. |
Applications
Architecture
Regular octagons are often used in architecture to create aesthetically pleasing designs. For example, the octagonal dome of the Hagia Sophia in Istanbul is one of the most famous examples of regular octagons in architecture.
Art
Regular octagons are also used in art to create geometric patterns and designs. For example, the octagonal star is a common motif in Islamic art.
Industries
Regular octagons are used in a variety of industries, including:
- Architecture
- Art
- Engineering
- Manufacturing
Essential FAQs
What is the difference between a regular octagon and an irregular octagon?
A regular octagon has equal side lengths and equal interior angles, while an irregular octagon has unequal side lengths and/or unequal interior angles.
How many diagonals does a regular octagon have?
A regular octagon has 20 diagonals.
What is the relationship between the side length and the apothem of a regular octagon?
The apothem of a regular octagon is half the length of the side.