Use the solubility table and classify – As we delve into the realm of chemistry, the concept of solubility emerges as a fundamental pillar, influencing a myriad of chemical processes and applications. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to master the use of the solubility table, a powerful tool for classifying compounds based on their solubility characteristics.
Through an in-depth exploration of solubility principles, the structure and interpretation of solubility tables, and the factors that govern solubility, this guide will empower you to confidently navigate the intricacies of compound classification.
Overview of Solubility
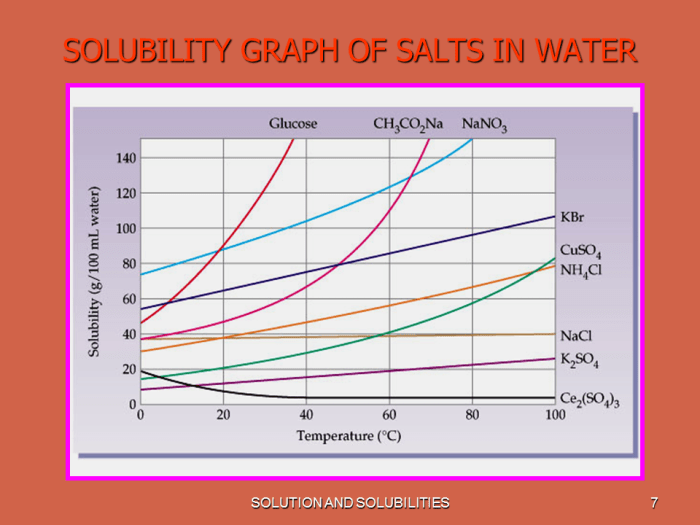
Solubility is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent. It plays a crucial role in various chemical reactions, industrial processes, and biological systems. Solubility is typically measured in units of grams per liter (g/L) or moles per liter (mol/L).
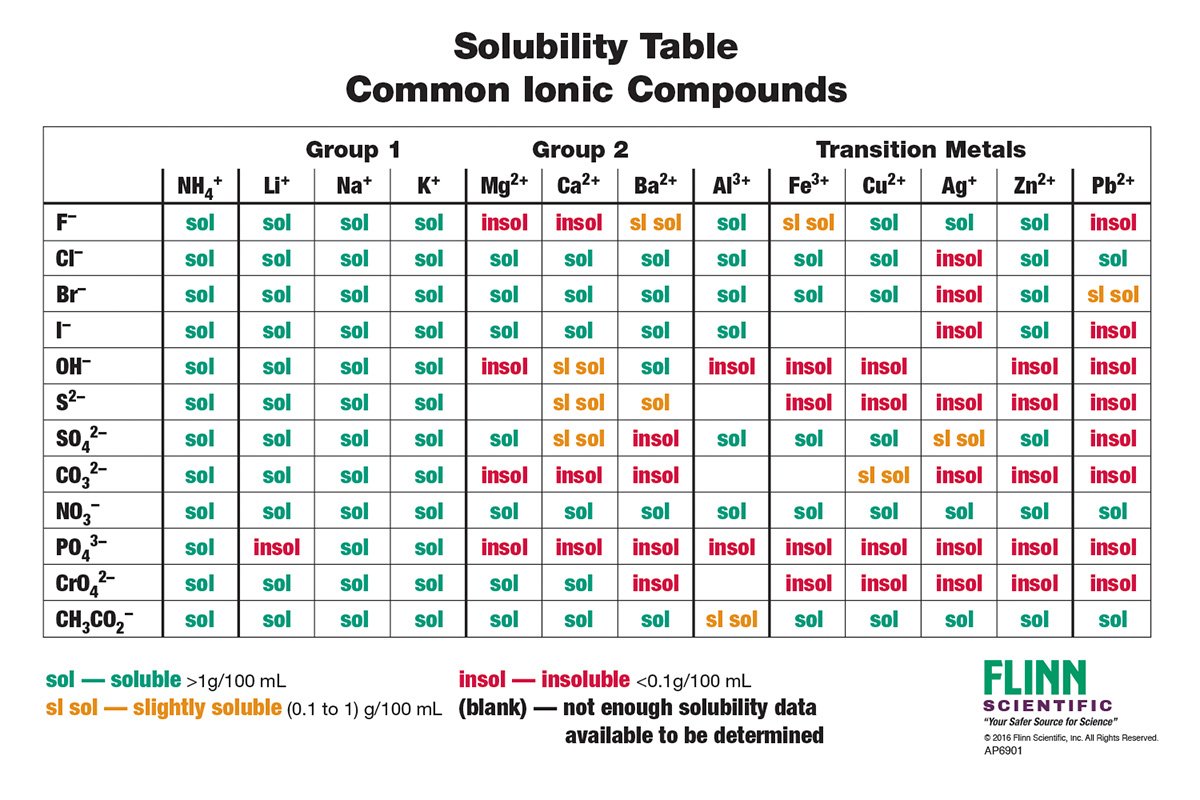
Solubility Table
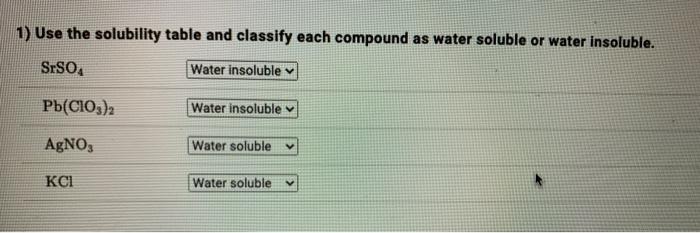
A solubility table is a valuable tool for classifying compounds based on their solubility in a particular solvent. It typically consists of two columns: one listing the solute (the substance being dissolved) and the other indicating the solubility of that solute in the given solvent.
Classification of Compounds, Use the solubility table and classify
Compounds can be classified into three solubility classes based on their solubility in water at room temperature (25°C):
- Soluble:Compounds that dissolve in water to a concentration of 0.1 mol/L or greater.
- Insoluble:Compounds that dissolve in water to a concentration of less than 0.001 mol/L.
- Partially Soluble:Compounds that dissolve in water to a concentration between 0.001 mol/L and 0.1 mol/L.
Examples of soluble compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), sugar (sucrose), and potassium permanganate (KMnO4). Examples of insoluble compounds include sand (silicon dioxide, SiO2), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3). Examples of partially soluble compounds include calcium sulfate (CaSO4), barium sulfate (BaSO4), and silver chloride (AgCl).
Factors Affecting Solubility
Several factors can influence the solubility of compounds in a given solvent. These include:
- Temperature:Generally, the solubility of solids and liquids increases with increasing temperature, while the solubility of gases decreases with increasing temperature.
- Pressure:The solubility of gases increases with increasing pressure. This is known as Henry’s law.
- Solvent Polarity:Polar solvents tend to dissolve polar solutes, while nonpolar solvents tend to dissolve nonpolar solutes. “Like dissolves like.”
Applications of Solubility
Solubility data has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals:Solubility is crucial for drug delivery and absorption.
- Food Science:Solubility affects the texture, taste, and stability of food products.
- Environmental Chemistry:Solubility is essential for understanding the fate and transport of pollutants in the environment.
FAQ Compilation: Use The Solubility Table And Classify
What is the significance of solubility in chemistry?
Solubility plays a crucial role in determining the reactivity, transport, and bioavailability of compounds in chemical systems.
How does the solubility table assist in compound classification?
The solubility table provides a systematic and convenient method for categorizing compounds into soluble, insoluble, or partially soluble based on their solubility data.
What factors influence the solubility of a compound?
Solubility is influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, solvent polarity, and the nature of the solute-solvent interactions.